Acknowledgements
I want to thank: My internship tutor Valerie Gallego that
trusted me for being able to accomplish the different
objectives of this internship. Professors Gilbert Farges and
Jean Pierre Caliste for leading and having accepted me in this
excellent master. Finally but not less
important to my parents Rosario and Juan Carlos for thrusting
and supporting me in all my plans and decisions.
List of Acronyms
DMP: Documentation Management Procedure
DSS: Documentation System Structure
PDCA: Plan-Do-Check-Act
GMP: General
Management Procedures
BPO: Business
Process Owners
Glossary
ISO 9001: Specifies the requirements for a quality
management system where an organization needs to demonstrate
its ability to consistently provide product that meet customer
and applicable statutory and regulatory requirements, and aims
to enhance customer satisfaction though the
effective application of the system, including processes for
the continual improvement of the system and assurance of
conformity to customer and applicable statutory and regulatory
requirements.
Management System: framework of processes and procedures used to
ensure that an organization can fulfill all tasks required to
achieve its objectives.
Quality of products and services: Expected outcome from the client, to reach all
their necessities in time and manner.
Documentation: Set of documents provided on paper, or online, or
on digital or analog media that permit achieving a specific
goal.
Top Management: Group of managers that have as main objective to ensure major business and financial decisions,
to allocate resources based on clear priorities and programs
Functional Departments: the
leaders of their functional community throughout the Group.
Return to Summary
Introduction
In every company a big amount of documents is handled such as:
procedures, standards, best practices, forms, memorandums,
etc. One of the most important documents is the Management
Manual. This manual shows the way the management system of the
company works.
According to the ISO 9001 norm
the specifications that a quality manual must have are:
· The scope of the
quality management system
· The documented
procedures or the reference to them
· A description of
interaction between the processes of the quality management
system
Since the specifications of the ISO 9001 norm are very
general, this allows the company to make a quality manual
according to its preferences, making possible to create a very
short management manual to accomplish the ISO requirements
[2]
.
In contrast to most documents within a company, the Management
Manual is a document that can be requested by costumers for
understanding the way in which the company meets the quality
requirements. It is advisable and sought by many companies to
have a “well-done” Management Manual which
meets the needs of informing all the essential information of
the management system of the company.
The objective of this
internship was to create a Management Manual at corporate
level which did not exist before as well as the analysis,
structuring and improvement of the Documentation System
Structure. To perform this task it was required to have a
great knowledge of the company, its
departments, methods, ways of working etc.
The Management Manual in question was not only intended to
inform all employees about the management system of the
company otherwise the vision, mission, values, way of acting
and strategies were other key points to inform the action of
the company with respect to the society in
which it lives.
Under the circumstances a PDCA method was used during all the
developing process, to have a methodological order, achieve
objectives in an efficient and ordered way and making easier
to transmit this knowledge for future projects
[3]
.
The methodology used to success the creation of a Management
Manual and Documentation System Structuring will be detailed
explained in this Methodological Memory.
Chapter 1
Company Overview
Who? - Nexans
Nexans
is dedicated to bring energy thought an extensive range of
cables and cabling solutions that deliver increased
performance for customer worldwide
[4]
.
What? -
Activities
Nexans offers:
· A complete range of cables, solutions and
services adapted to your needs.
· A presence on all continents to assure you of
global reach and local proximity.
· A strong R&D organization dedicated to
innovation on your behalf.
Nexans has 4 major core businesses:
· Energy and Data Infrastructure (40%):
o High-, medium-
and low-voltage submarine, underground and overhead
electricity transmission and distribution networks
o Land-based and
submarine telecommunication networks, using copper and optical fiber cables.
· Energy Resources (10%):
o On- and off-shore
oil and gas
o Renewable
energies: On- and off-shore wins farms and solar power
· Transport (14%):
o Aeronautical and
spatial
o Automotive
o Shipbuilding
o Rolling stock and
railway networks
o Airports, railway
stations and ports
· Building (24%):
o Industrial,
logistics, tertiary and commercial buildings
o Collective
buildings
o Housing
o Data centers
Where? –
Locations
Serving a range of different types of customers – including
network operators, energy producers, mining companies,
engineering firms, equipment manufacturers, installers and
distributors, and infrastructure and construction companies –
which have
local, regional or even global needs.
Manufacturing sites in 40
countries across 5 continents.
Figure 1 - Sites around the world
[4]
Return to Summary
When? –
Actual Situation
The teams help meet these vital needs for 21st century society
by providing high-performing, cost-efficient and long-lasting
solutions for the most complex of uses and the most demanding
of environments.
How? –
Technological Leadership
Through the combination of technological leadership, global
expertise and local presence, that can effectively partner our
customers’ development projects, offering them the best
conditions for achieving their objectives while respecting the
highest levels of safety and taking
the greatest possible care of people and
the environment.
Why?
– Energy to function
Day to day the world requires more energy to function, develop
and achieve higher living standards. For over a century Nexans
has played a key role in providing the energy that people
need.
Cables are an indispensable part of today’s connected towns and
cities, providing access to energy, creating communication
channels, facilitating the movement of goods and people, and
ensuring the comfort and safety of the
infrastructure and
buildings that are essential for development and improving the
quality of life.
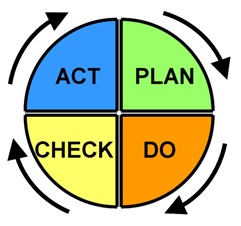
PDCA Method
The PDCA (Plan – Do – Check – Act) is a quality iterative
method developed by Dr. Edwards Deming that allows
developing projects, always looking forward for continuous
improvement. It is also known for developing critical
thinking and creating a culture of problem solving
[3].
Figure 2 - Sites around the world
[3]
It is divided in four main steps:
Plan: To plan what
is intended to do. It is necessary to establish the
objectives, the output expectations and get to know the
tools that are going to be used during the realization of
the intended project.
Do: Work on what
was planned in the first step. Modifications of the planning
can be done if it increase efficiency or improves the
project in a certain way.
Check: Measure and
analyze the obtained results in the second step (DO).
Compare them with the expected results in the first step
(PLAN).
Act: Improve and
evolve. Involves making
adjustments or corrective actions to the revisions done in
the step 3 Check.
This method is used:
· When starting
a new improvement project.
· When planning
data collection and analysis in order to verify and
prioritize problems or root causes.
· As a model
for continuous improvement.
· When
developing a new or improved design of a process, product
or service.
· When
implementing any change.
For creating a new improvement project such as a Management
Manual or a Documentation System Structuring that have to be
always improved and updated (at least every year) the PDCA
is a very powerful, useful and efficient methodology.
While other methods for problem solving such as project ISO
21500 can be very complex and take a lot of time to
understand how they work, the PDCA is simple and it can be
easy to explain and understand by everyone in a short lapse
of time. Major advantages over other
methods are:
· Espouses the
cause of continuous improvement.
· Helps
eliminate mistakes.
· Improves
productivity.
· Does away
with complacency.
This method was implemented for the realization of this
project and it is going to be explained in detail in the
next chapters of this document.
STEP 1 –
PLAN
To begin the realization of the first step PLAN of the
method it was necessary to establish objectives and limits
for the project. Making a plan of what is going to be done
and deciding how this plan is going to be successfully
completed are the firsts parts to be developed
[3]
.
To perform this first step the problems and objectives were
deeply analyzed to understand what the exact goals of this
project were and begin the realization of an action plan.
The different stages of the first part of the PDCA (PLAN)
method are explained in detail in the next sub-chapters
regarding the next subjects:
· Problem Explanation
· Objectives and Deliverables
· Context of the Project
Return to Summary
Problem
Explanation
The company as is an
international entity that has had a very fast growth during
the last years in the cable industry, having nowadays; 26, 000
employees, 6.4 billion euros in sales and manufacturing sites
in 40 countries
[4]
.
Each plant around the world is dedicated to develop different
products depending on the specific needs of the local
costumer. To fulfill the quality that each customer is
expecting, each plant develops its own work practices and
documentation.
As every international company general management
documentation is necessary to govern with general rules and
common practices that everyone in the company around the world
must abide and respect.
For this reason the top management was looking forward to
organize, standardize and communicate the general management
practices and documentation to increase productivity and
making communication and development easier between the
different plants and
departments around the world within the
company.
To achieve this objectives the management proposed to
create a set of documents that would summarize and
communicate in a clear manner management practices and
documentation.
Objectives and
Deliverables
The objective of this internship was to develop a group of
management documents that will be diffused and communicated
all around the world, explaining in a detailed, clear and
easy way how general management works day by day.
To fulfil this necessity two deliverables were expected to be
done by the general management:
· Management
Manual: A document that contains key information about
the company. This manual has as main objective to inform all
employees how the group works at a management level.
· Documentation
System Structuring: Research, order,
name and classify the different documentation available at
group level and making it reachable to all employees around
the world.
Return to Summary
Context
of the Project
The creation of the deliverables, Management Manual and the
Documentation System Structuring are tasks that couldn’t be
done by a single person or resource. Key factors were needed
to succeed:
· Collaboration
between managers of the different departments at Group level
and other key people as quality experts.
· Deep knowledge of
the enterprise, its documentation and way of working.
A cause and effect diagram was created to identify the
different causes involved in the creation of the deliverables.
Each of the causes are going to be explained in detail
[5]
:
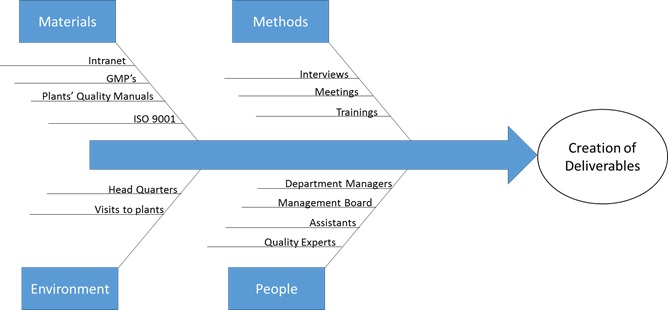
Figure 3 - Context Cause & Effect
Diagram
[5]
Materials
As in
any project there were materials and tools that were key for
succeeding. The most important materials and tools utilized in
this project were:
Return to Summary
The Intranet
As specified in the ISO 9001:
4.2.3 Control of documents
Documents required by the quality management system shall be
controlled.
A documented procedure shall be established to define the
controls needed
[2]
:
a) To approve documents for adequacy prior to
issue
b) To review and update as necessary and
re-approve documents
c) To ensure that changes
and the current revision status of documents are identified
d) To ensure that relevant versions of
applicable documents are available at points of use
e) To ensure that documents remain legible
and readily identifiable
f) To ensure that documents of external origin
determined by the organization to be necessary for the
planning and operation of the quality management system are
identified and their distribution controlled
g) To prevent the
unintended use of obsolete documents and to
apply suitable identification to them if they are retained for
any purpose
The control of documents in the company is managed in an
Intranet that is widely used by all employees all around the
world. The number of
active users of the group intranet has almost tripled to
10300, while the number of page views has risen 30% to 1.3
million. It is calculated having an average
of 5000 visits per day and all employees are have an
Intranet’s usage training at their entrance to the company
[6]
:
Figure
4 - Intranet Example 1
[6]
Figure 5 - Intranet Example 2
[6]
Mostly all of the content concerning the Management Manual and
the Documentation System Structuring was extracted from
different documents available in the group’s Intranet. The top
management and every department have to have most of their
documents concerning to its work, and
practices updated.
Some exercises were done to facilitate the discovery of the
Intranet. The dynamic of one of the exercise, was about
looking for some specific topics to be used in the next months
related to project’s goals, chronometer the time used to find
them and specify the location of each
document (See Annex B for more details).
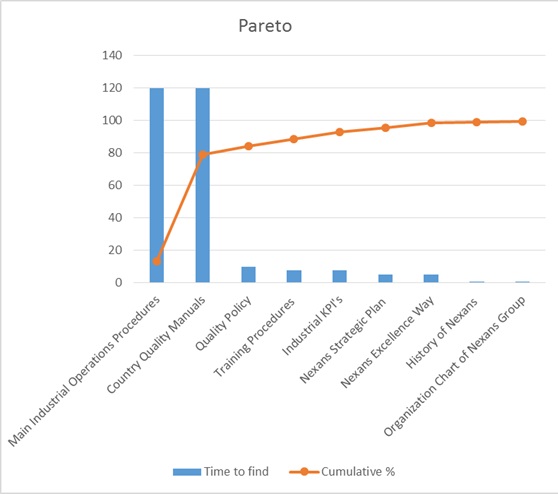
A Pareto Chart was created to make an analysis between the
different topics vs the time taken to find information about
them in the Intranet:
Figure 6 -
Pareto Chart Time VS Documentation
[7]
As it can be seen in the graphic Pareto Principle applies,
meaning that 80% of the time was used to find around 20% of
the information. The result of this analysis allowed to
discover the documentation that will have to be treated with
specific departments and persons since it
wasn’t fully available in the Intranet
[7]
.
This analysis was very useful, after analyzing the results,
Procedures and Quality Manuals were not fully available in the
Intranet, having to give priority to appointments with key
people for the collection and analysis of this documentation,
since the rest was fully available in the
Intranet.
Return to Summary
General
Management Procedures
14 Management Procedures concerning the most important
activities, practices and rules in the Company. This
procedures are applicable at any level in the company. Reading
and analyzing this procedures was essential to get to know the
enterprise and to have a guide of how
deliverables had to be redirected according to general
practices.
Quality
Manuals
It is mandatory for every plant around the world to have a
Quality Manual since they were all ISO 9001 certificated.
Analyzing and comparing the content of the different Quality
Manuals helped in the writing of deliverables in various ways:
· Analyzing the
quality policies and quality requirements of costumers around
the world.
· Understanding the
content that a Quality Manual should include (ISO
requirements).
· Including certain
content in the Management Manual.
ISO 9001
Analyzing and understanding the ISO 9001 was fundamental for
de writing of the deliverables, since it specifies the
requirements for the quality management system of an
organization.
To understand this norm, an excel document was done, making
reference to each chapter of the norm, mentioning what is it
about with a small description and finally specifying the
different mandatory procedures and the procedures that shall
be established. (See Annex A).
After this analysis, two subchapters highlighted concerning
the objectives of the project:
4.2 Documentation Requirements
4.2.1 General
a) Documented statements of a quality policy and
quality objectives
b) A quality
manual
c) Documented
procedures and records required by this International
Standard
d) Documents,
including records, determined by the organization to be
necessary to ensure the effective planning, operation and
control of its processes
4.2.2 Quality
Manual:
The organization shall establish and maintain a quality manual
that includes:
a) The scope of the quality management system,
including details of and justification and justification for
any exclusions
b) The documented procedures established for the
quality management system, or reference to them
c) A description of the interaction between the
processes of the quality management system
These two subchapters of the ISO 9001 make reference to
certain goals that were essential for the realization of the project
[2]
.
Return to Summary
Methods
Interviews
& Meetings
Contacting key people was fundamental for obtaining specific
information and documentation that had to be included in the
deliverables. The contacts’ information was given the first
week of the internship by the tutor and they were contacted in
different time lapses
depending on the progress and necessities for the manual.
Most people to be contact were managers of the different
departments and business process owners as the have key
management information. Appointments with key people were
normally done with anticipation due to the tight agenda of
most them. If
they were not
available appointments with direct assistants or employees
that were experts in the subject were requested, assuring that
a discussion will take place and the information in the
deliverables would be truthful coming from a thrusted source.
A flow chart diagram was created to explain the way of
contacting people for assuring the availability of the
different content required in the deliverables
[8]
:
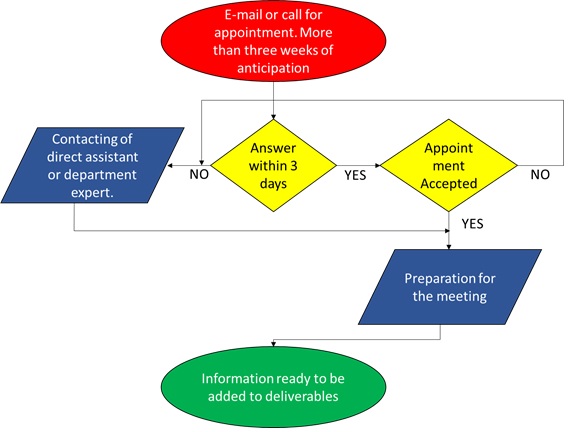
Figure 7 -
Flowchart for making appointments
[8]
Trainings
Two trainings were taken during the development of the project
to strength certain abilities that were essential for its
realization:
· How to
do process mapping: Two days
training explaining the reason and best ways to create process
mappings.
· How to
communicate: One day training
that explain the basis of communication and how to get better
applying them.
The acquired knowledge was utilized during the whole project,
since communication and good understanding with different
people was fundamental to achieve the goals proposed.
Environment
Headquarters
Headquarters were the place where mainly all the work was
done. There were evident advantages of working in Headquarters
[9]
:
· Managers and key
people were situated in headquarters.
· Trainings took
place in headquarters.
· Easy access to
archives of management documentation.
Visits to
Plants
Three visits to different plants took place during the
project. The main objective of these visits was to discuss the
content of the deliverables create new ideas and validate
information with different quality experts in different places
in France and Europe
[4]
.
The
places where the visits took place:
· Hannover, Germany.
· Charleroi,
Belgium.
· Calais, France.
Return to Summary
People
Involved
A Process Mapping of the group was created to make a deep
analysis of what and who was involved in at management level
[10]
:
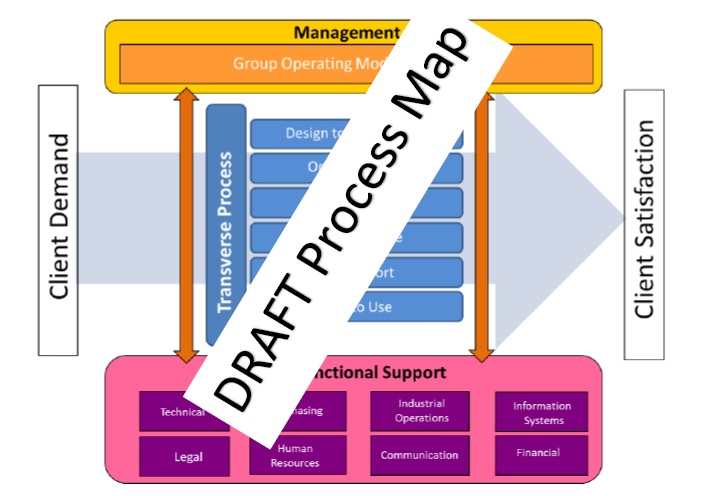
Figure 8 -
Company Process Mapping
[10]
According to the different processes that can be seen in the
Groups’ Process Mapping the people involved in the creation of
the deliverables were:

Figure 9 -
People and Departments Involved
[4]
All the
people mentioned before was contacted successively for
different reasons as:
· Gathering,
analyzing and revising information.
· Revising the
status and correcting deliverables.
· Upgrading
documentation.
· Validation of the
deliverables.
Success
Criteria
It was essential to have precise characteristics, qualities
and attributes to be able to succeed the correct creation of
deliverables according to the difficulties presented:
· Understanding
and defining the project: Understanding what does the management was expecting of the
deliverables and what where the real needs of the company to
be able to make a program and achieve expectations on time and
form.
· Understanding
the different needs and points of view: The general management, the managers of the
different departments and the quality experts had different
needs and opinions about the content of the deliverables. One
of the main tasks was to understand this opinions and unify
and modify them to have the best possible result.
· Working
as a link between people: To
communicate the different needs and opinions of the different
people concerned was essential to make others understand the
different necessities and align them with theirs.
Risk Analysis
When planning and developing the project some events might
have occurred risking its realization. Knowing what those
risks might be and implementing measures to prevent or
minimize them was essential for finishing the project in the
scheduled time and fulfilling all
demands.
To determine how to reduce or avoid those risks, a risk
analysis methodology was implemented to analyze possible
solutions and its feasibility of implementation (See Annex C
for the complete table).
After a deep analysis three main risks were found that could
have affected the realization of the project:
1. Documentation
written in several ways: Some terms, definitions and concepts had been
written in several ways by different people presenting the
same general idea with different wording.
2. Documentation
not updated or not easy available: Some documents were not recently updated or ere
archived by specific persons that did not make these documents
available for everyone.
3. Not
being able to work with certain people: Certain people were not able to revise and work
for the Management Manual content since there is no
availability on their agenda.
Preventive actions for main risks:
1. Use published information in official
documents. If the same information with different working is
present in several official documents a meeting with the
person in charge of the subjects has to be done to decide
which information is more suitable.
2. Contact people to update or ask for the
desired documents with anticipation.
3. Make appointments with managers with
anticipation, if not possible, make appointments with the
second in charge or direct assistants.
Return to Summary
Chapter 2
STEP 2 - DO
After having understood the problem and establishing clear
objectives. The creation of the Management Manual and the
Documentation System Structure were begun. As it can be seen
in the program this step is the one that lasted more and is
the core of the project
[3]
.
The main tasks for the second part of the PDCA (DO):
· Way to proceed
· Program
· Writing of the
Management Manual
· Writing of the
Documentation System Structuring
Way to Proceed
Once objectives were clarified the general steps for the
realization of the process were traced. A process mapping of
the project was done to identify the inputs, outputs,
departments, people and the general processes involved for the
realization of the project
[10]
.
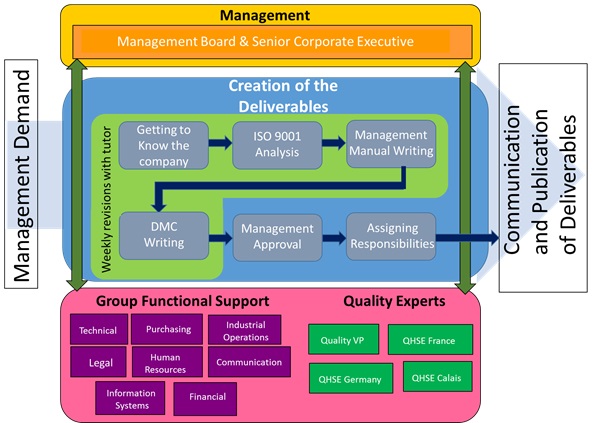
Figure 10 -
Project's Process Mapping
[10]
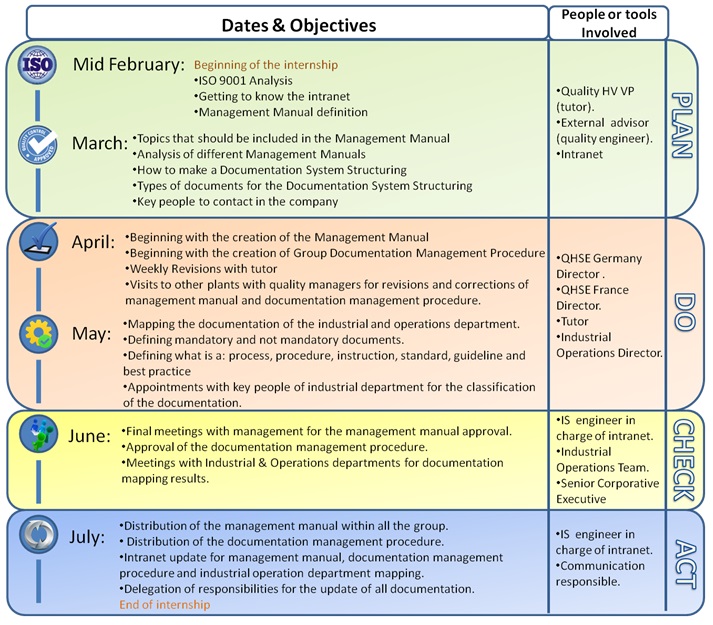
Program
A planning was created together with the internship’s tutor to
clarify and schedule the different activities to perform
during the 6 months duration of this project.
This program was not totally fixed, dates and actions could
have had minor changes because of the agendas of the people
involved or for improving efficiency at the moment of
developing the activities.
Management Manual
Quality
Manual VS Management Manual
The ISO 9001 was used for defining the beginning of the
project until it was decided to create a Management Manual for
the reasons presented below:
According to the norm ISO 9001, the requirements that a
quality manual must have, can make this manual a very simply
document that has just to mention the scope of the management
system, include or make reference to the established
procedures for the quality manual
and have a description of the interaction
between the quality management processes.
The main objective to managers in the company for creating a
manual was to:
· Give a
reference of the management behavior.
· Implementation
of the company’s management rules and practices.
· Standardize
common practices within the company.
· Make this
document to be applicable to the full company organization
including worldwide subsidiary sites concerning all
employees and members of the staff in the company.
· A document that
everyone in the company was able to understand.
As the different objectives demand more requirements than the
ones required in a Quality Manual (including them) it was
decided to create instead a Management Manual, term that fits
better for these purposes
[2]
.
A Management Manual is a document that
shows how all the management system in a company is organized.
From among all the documents comprising the management system
of the company the Management Manual is the most important
[1]
.
Content
6 main chapters were written to fulfill groups’ needs in the
best possible way covering most sensible topics for describing
the management and general rules. The final version of the
Management Manual Summary
[1]
:
Summary
1. THE
COMPANY: Presents the most important general information of
the company.
Overview
Vision Statement
Values
Vision
How we act
Strategy
History
2. THE
PRODUCTS: Presents the different product categories and market
segmentations within the company.
Product Segmentation
Product Categories
Market Segment
Customer Dimensions for
Market Segmentation
3.
MANAGEMENT MODES: Explains how
and why management acts and works.
The Group Operating Modes
Nexans Organization Chart
2014
Roles and responsibilities
in Group Organization
Business Divisions Level
Operational Units Level
Group Level
The Group Management Board
Governance and Committees
Performance Steering Modes
Operating Modes across
Divisions
4. THE
GROUP FUNCTIONAL SUPPORT: Describes
the departments involved in the management.
Group Functions
Business Process Owners
(BPO’s)
Other Committees,
dedicated to coordinating the implementation of policies
5.
MANAGEMENT SYSTEM: Process
mapping and structuration of the general management system
The System
The System Structure
6.
GENERAL MANAGEMENT PROCEDURES (GMP’s): Procedures that are
applicable at any level in the company.
Annex
Follow-up of changes
Glossary
The explanation of all the chapters is not going to be
detailed in this document since it is intended to explain the
methodology used for the creation and not the content itself.
Return to Summary
Documentation System
Structuring (DSS)
Organizing, structuring and recording documentation is
fundamental in any company. These tasks are successfully done
at countries and plant levels in the company; nevertheless at
group level this structure was not clear and never formalized.
In order to create a solid
Documentation System Structure a new Group
Documentation Management Procedure and other specific
activities were performed
[1]
.
Documentation Management Procedure (DMP)
The purpose for the creation
of the DMP at group level is to describe how the documentation is structured,
written, verified, approved, referenced, modified, archived
and destroyed.
The objective is to
standardize the documentation with clarity and simplification
in order to improve our efficiency at Group Level.
It was intended that all the
existing documents will be gradually upgraded to compliance
with this procedure when they will be reviewed.
This procedure had to apply to
every function at Group level.
The general content of the
DMP:
· Management
System: Process mapping of the
whole Management System within the group.
· Documentation
Structure: Description of the
four levels of documentations, details can be found in the
chapter below.
· List of
documentation: The listing and
classification of all the documents in the management and all
functional departments.
· Documentation
definitions: Description of
the characteristics for every document at Group Level.
· General
Rules: Explains some general
rules that every document must have such as:
o Documentation
Format
o Modifications
o Codification
o Circulation and
Availability
o Confidentiality
Documentation
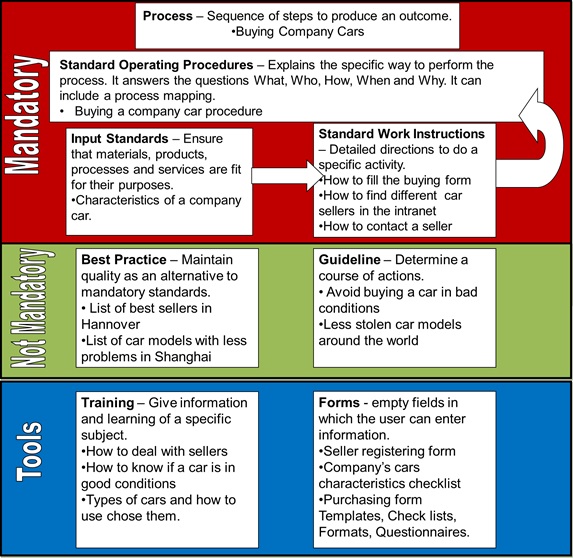
Structure and Organization
According to the DMP all
the documentation at group level including functional
departments had to follow the Group’s Documentation
Structure (see Figure 12). This structure has 4
main levels:
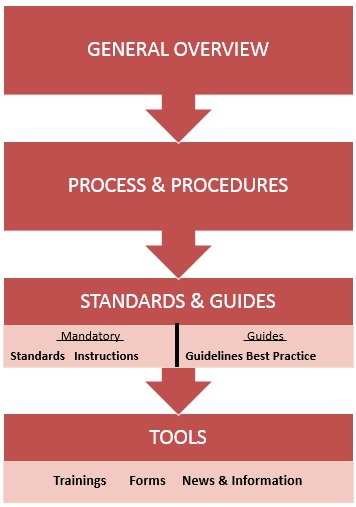
Figure 12 -
Documentation Structure
[11]
1. General
Overview: Set of documents
that provide general information of the General Management or
Functional Departments some example of these documents are:
· Management Manual
· List of documents
2. Process
& Procedures: Document
that provides requirements, specifications, guidelines or
characteristics that can be used consistently to ensure that
materials, products, processes and services are fit for their
purpose.
3. Standards
& Guides: Mandatory and
good to have documents are included in this sections more
information can be found in the next sub-chapter.
4. Tools: Documents that help achieving a particular tasks
or facilitate the creation of documentation such as:
· Trainings
· Presentations
· Formats
· Questionnaires
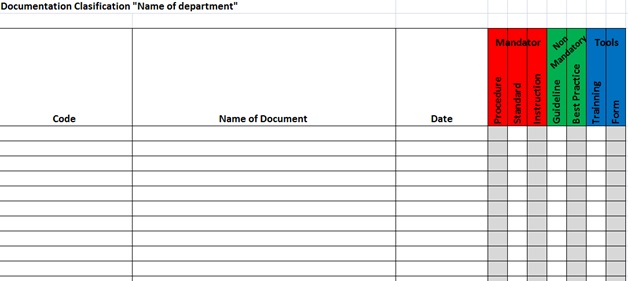
This structured was used to organize all documentation the in
the different departments, classifying the available documents
with a check list.